A practical guide to growing your opening database with real games
Introduction
An opening book is one of the most powerful tools inside Fritz. It allows the engine to play strong, theory-based moves instantly in the opening phase, instead of calculating everything from scratch.
If you’ve downloaded PGN game collections from websites (which is exactly the right place to start), you can use them to expand and strengthen your Fritz opening book, making it richer, deeper, and more up to date with modern theory.
This guide walks you through the full process—step by step.
Step 1: Get High-Quality PGN Files
Yes, you start exactly where you suspected: PGN databases.
Good sources include:
Online chess game repositories
Tournament databases
Engine vs engine tournaments
Your own played or analyzed games
💡 Tip:
The quality of the opening book depends on the quality of the games. Prefer:
Grandmaster games
Engine tournament games
Recent games (last 5–10 years)
Step 2: Import the PGN into Fritz / ChessBase

Fritz works hand in hand with ChessBase.
Open Fritz
Go to File → Open → Database
Open (or create) a database where you’ll store the PGN games
Import the PGN:
File → Import → PGN
Select your PGN file
Let Fritz convert it into a ChessBase database
Once imported, you should see all games listed and playable.
Step 3: Create or Select an Opening Book
Now comes the key part.
Go to Tools → Opening Book → Create New Book
(or load an existing.ctgbook)Give the book a name (example:
My_Expanded_Openings.ctg)Choose a location (default ChessBase Books folder is recommended)
This .ctg file is your actual opening book.
Step 4: Add Games to the Opening Book
This is where your PGN games become opening knowledge.
Open the database containing your imported games
Select the games you want to include:
Ctrl+A to select all
Or manually select only high-quality games
Go to:
Tools → Opening Book → Add Games to BookChoose your
.ctgopening bookLet Fritz process the games
Depending on the size of the PGN, this may take a few seconds or several minutes.
Step 5: Adjust Book Settings (Very Important)
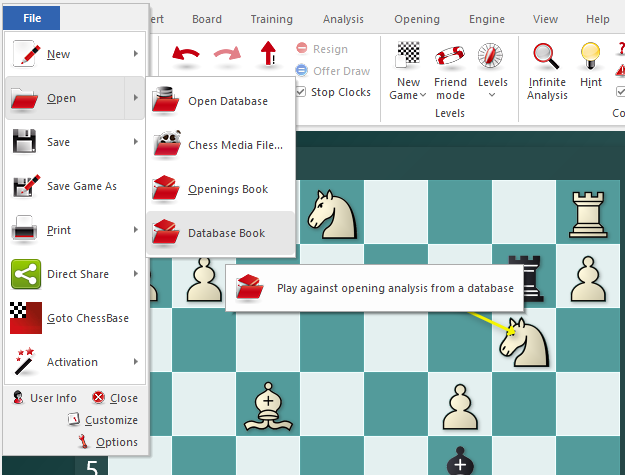
After adding games, you should fine-tune how Fritz uses them.
Open Opening Book Settings and adjust:
Minimum Games (e.g. 2–5)
Weight by Elo (recommended ON)
Ignore short draws (strongly recommended)
Prefer main lines (optional, style-dependent)
💡 This step prevents weak or dubious lines from polluting your book.
Step 6: Test the Expanded Opening Book
Now test your work.
Start a new game with Fritz
Make sure your custom opening book is selected
Observe:
Does Fritz play deeper theory?
Does it stay “in book” longer?
Are opening choices more varied?
You can also:
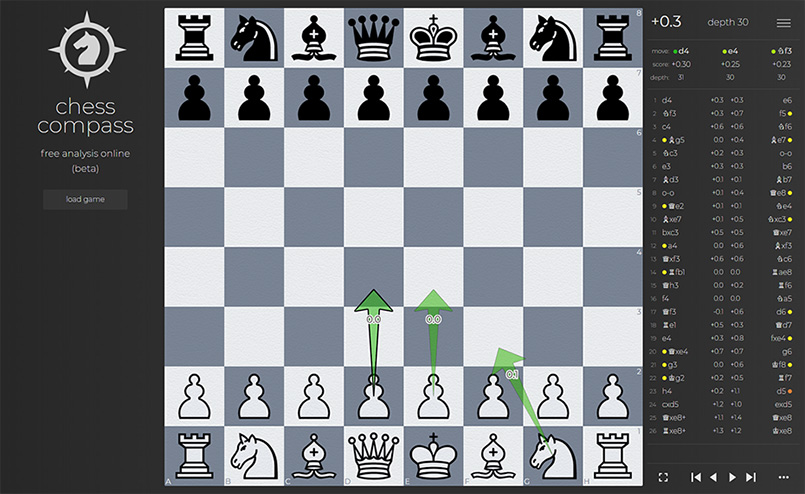
Enter Analysis Mode
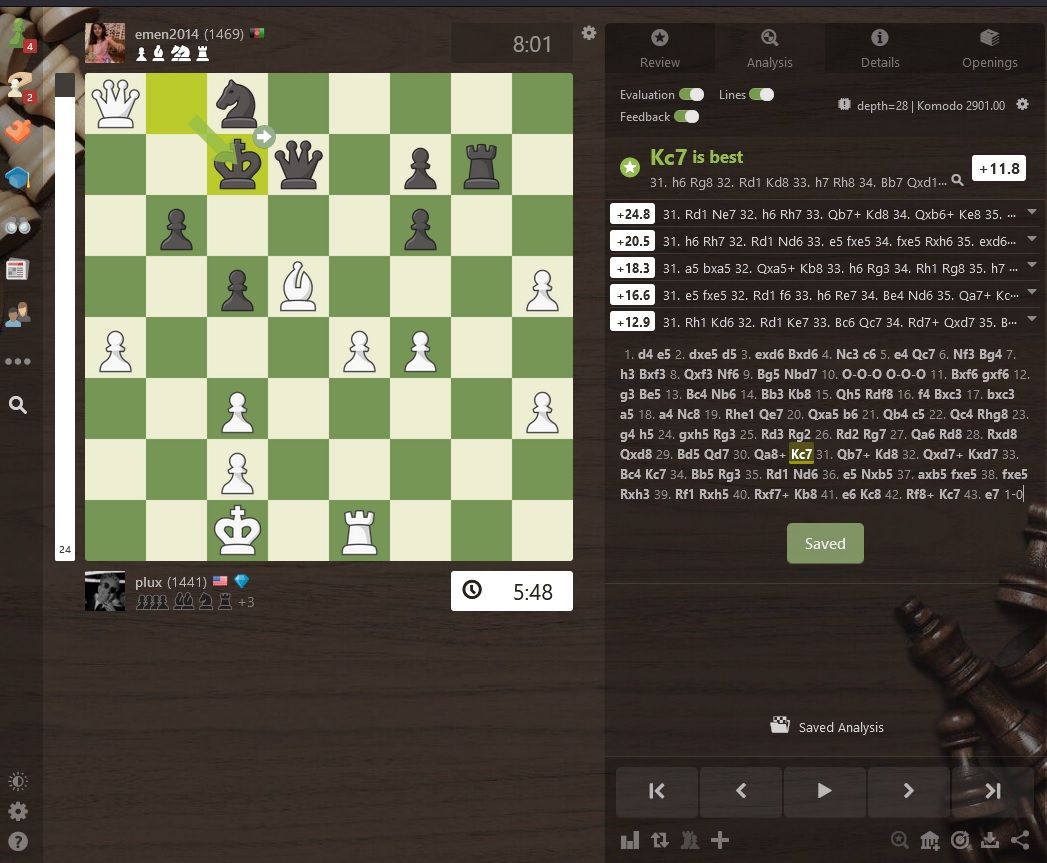
Navigate opening positions manually
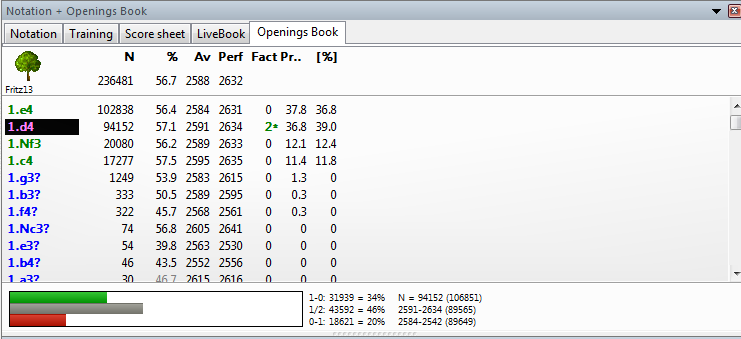
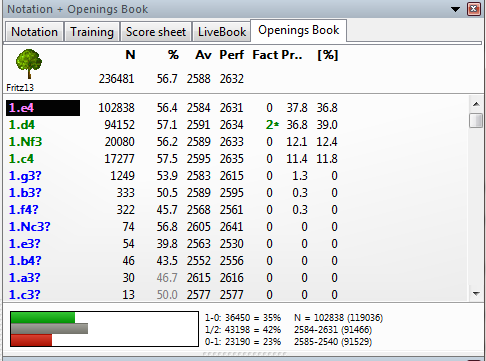
See statistics: win rates, draws, popularity
Step 7: Keep Improving the Book Over Time
An opening book is never finished.
Best practices:
Periodically add newer games
Remove outdated or refuted lines
Maintain separate books for:
Classical chess
Blitz / Rapid
Chess960
Many advanced users keep multiple opening books depending on purpose.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
🚫 Adding low-quality blitz games
🚫 Mixing engine test games with human games randomly
🚫 Forgetting to weight games by Elo
🚫 Overloading the book with too many weak sidelines
A smaller, cleaner book often plays stronger than a massive messy one.
Final Thoughts

Expanding an opening book in Fritz is not just technical—it’s strategic.
You are shaping:
What Fritz plays automatically
How it understands modern theory
Which positions it reaches most often
With well-chosen PGN files, your opening book becomes a silent coach, guiding every game before calculation even begins.
SEO Tags
Tags: Fritz opening book, ChessBase opening book, PGN to opening book, chess engine openings, Fritz tutorial
Hashtags: #FritzChess #OpeningBook #ChessBase #PGN #ChessEngines #Ajedrez